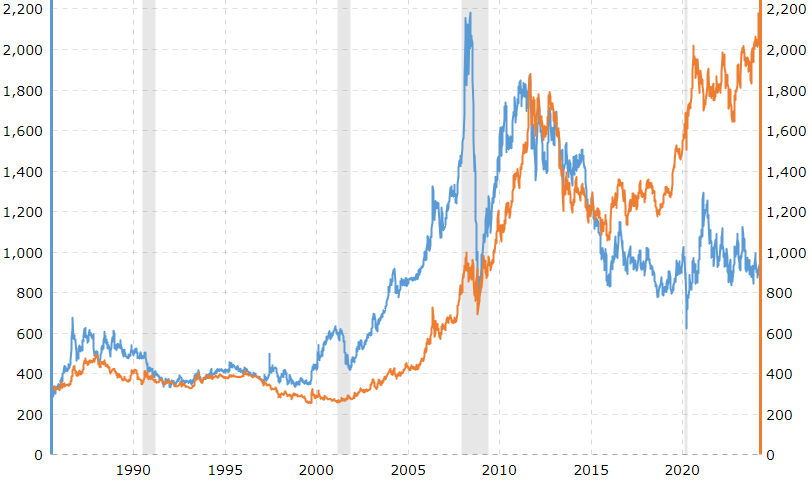
Gold and platinum prices from Aug. 12, 1985, to March 11, 2024, where gold hit a peak of $2179.47 on 3/11/2024, $2231.56 on 3/25/2024, and $2249.45 on 4/1/2024.
Gemstone Chemistry
Gemstones include ruby, sapphire, and emerald, and precious metals include gold, silver, platinum, and diamond. Do not mix jewelry with bleach, meaning do not wear them when you go into swimming pools.
1. What's the chemical difference between ruby and sapphire?
Ruby and sapphire are both forms of the mineral corundum, which is the crystalline form of aluminum oxide (Al2O3). Ruby gets its red color from the presence of chromium and sometimes iron, while sapphire can come in a variety of colors including blue (from iron and titanium), pink (from chromium), yellow (from iron), green (from vanadium and chromium), purple (from iron and titanium), and colorless (pure corundum with no impurities). A rare type of sapphire, padparadscha sapphire, is pink-orange. Pure corundum has a hardness of 9.0 on the Mohs scale, and a density of 4.02 g/cc, which is unusually high for a transparent mineral composing of aluminum and oxygen.
2. What about for emerald?
Emerald is a variety of the mineral beryl, which has the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. The green color of emerald is due to the presence of trace amounts of chromium, vanadium, and iron, as well as the presence of water in the crystal structure. It is a cyclosilicate.
The specific green color of emerald is a result of the way the chromium and vanadium impurities absorb and reflect light in the crystal lattice. The presence of iron can also affect the color of emerald, producing a bluish-green or yellowish-green hue.
3. Can ruby or sapphire be green?
Yes, sapphire and ruby can be green, but they are typically not referred to as sapphires or rubies in the gemstone industry.
The green variety of corundum is known as green sapphire or green ruby, depending on the specific shade of green. Green sapphire can occur naturally or can be produced by heat treating yellow or blue sapphire. Green ruby, on the other hand, is typically created by artificially treating low-quality ruby with heat and flux, which can remove the red color and create a green hue.
Green sapphire and green ruby can come in a range of shades, from light green to dark green, and can have varying levels of saturation and clarity. They are both valued for their unique and attractive green color, and can be used in jewelry just like any other gemstone. However, because they are not the traditional red or blue colors associated with sapphire and ruby, they are typically marketed under their own names rather than being referred to as sapphires or rubies.
4. Can emeralds be red or blue?
While it is technically possible for emeralds to be red or blue, these colors are extremely rare and are not typically seen in natural emeralds.
In some cases, beryl crystals that are red or blue can be marketed under specific names. For example, red beryl is also known as "bixbite" or "red emerald," while blue beryl is known as "aquamarine." However, these stones are not true emeralds and do not have the same chemical composition or crystal structure.
It's worth noting that there are some synthetic or lab-created emeralds that have been produced in shades of red or blue. However, these stones are not natural and are typically created using a different process than natural emeralds.
5. Is there a purple equivalent to emerald?
Yes, Alexandrite, a rare variety of the mineral chrysoberyl, which has the chemical formula BeAl2O4. It was first discovered in Russia in the 19th century and is named after the Russian Tsar Alexander II.
Alexandrite is known for its remarkable color-changing properties, where it can appear green in daylight or fluorescent light and change to a reddish-purple color in incandescent light. The color change is due to the presence of chromium and iron impurities in the crystal lattice, which absorb different wavelengths of light depending on the light source.
The specific shade of purple in alexandrite is due to the combination of iron and chromium impurities, which give the gemstone its unique and highly prized color. Alexandrite is a rare and valuable gemstone, and its color-changing properties make it one of the most sought-after gems in the world.
However, alexandrite is not typically considered a purple gemstone. For purple gemstones, amethyst is one of the most common and popular options. Amethyst is a type of quartz that ranges in color from pale lavender to deep violet, and is relatively abundant and affordable compared to some other gemstones.
Other popular purple gemstones include tanzanite, which is a relatively new gemstone discovered in Tanzania in the 1960s, and purple spinel, which is a rare and highly prized gemstone known for its intense color and high clarity.
6. Can rubies or sapphire be purple?
Typically no, if you are specifically looking for a purple gemstone, there are many other options available, such as amethyst, tanzanite, and purple spinel
7. Will the electronics industry that buy gold and copper, also buy ruby, sapphire, emerald?
Typically no, as these gemstones do not have the necessary electrical or thermal properties required for electronic components. However, there are some industrial applications where synthetic corundum (the mineral that makes up ruby and sapphire) can be used as a material for various purposes, such as abrasives, optics, and high-strength components. In these cases, synthetic corundum can be produced to specific specifications and can be tailored to meet the needs of the particular application.
The demand for synthetic corundum for industrial applications is relatively small compared to the demand for gold and copper in the electronics industry. Gold and copper are highly conductive materials that are used extensively in electronic components such as wires, connectors, and printed circuit boards.
8. Who is the most expensive?
High-quality rubies have been considered the most valuable of the 3 gemstones, especially those with a rich, deep-red color known as "pigeon's blood." Some of the world's most famous rubies, such as the Sunrise Ruby and the Hope Ruby, have sold for millions of dollars at auction.
However, there are also some extremely valuable sapphires and emeralds on the market. For example, the Blue Belle of Asia Sapphire, which sold for over $17 million at auction, and the Rockefeller Emerald, which sold for over $5 million.
9. What is metallurgy?
In the context of the jewelry industry, metallurgy plays an important role in the production of precious metal alloys, such as 18-karat gold or sterling silver, which are commonly used in jewelry making. Metallurgy is also important for understanding the properties and behavior of metals in different settings, such as during the soldering or welding of jewelry components.
Sterling silver is 92.5% silver, with 7.5% (by weight) of another metals, usually copper.
10. What is the value of gemstones?
Unlike diamonds, gemstones have no universally-accepted grading system. Diamonds are graded using a system developed by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) in the early 1950s.
11. Who's more expensive, gold or platinum?
They can cross each other. From the late 1990s to the early 2010s, platinum was more expensive than gold, peaking at over $2,000 per ounce in 2008 (1 oz is 28 g). However, gold has been more expensive than platinum since 2015. As of Sept. 2021, 1 g of gold is worth $43, 1 g of platinum $27 (or $765 per ounce).
Aug. 2011 is when gold surpassed the price of platinum (July 2011 Au $1613 Pt $1779, Aug. 2011 Au $1862, Pt $1855), but Pt was last worth more than gold in Sept. 2014 (Pt $1406, Au $1264), and ever since then, by October, gold is worth more.
In early 2021, the price of rhodium exceeded $20,000 per troy ounce, making it more expensive than gold, platinum, or palladium.

Gold and platinum prices from Aug. 12, 1985, to March 11, 2024, where gold hit a peak of $2179.47 on 3/11/2024, $2231.56 on 3/25/2024, and $2249.45 on 4/1/2024.
Here's why gold prices went up in early 2024.
Gold prices tend to fall when the dollar increases and they tend to rise when the dollar decreases. Therefore, gold prices were crushed during most of 2022, as interest rates were rapidly rising and the dollar was strengthening. Another factor that continues to help drive prices higher is central banks buying gold: an increasing amount of it. Many central banks have been buying more gold because they believe it may hold its value better than currencies and bonds, and to help provide diversification with other financial assets.
In 2021, central banks held about 1/5th of all the gold that's ever been mined, or about 35,000 metric tons. The International Monetary Fund holds about 2,814 metric tons of gold valued at about $158.5 billion.
12. Are gemstones and precious metals damaged from sunlight?
UV light is not harmful to gold, silver, platinum, ruby, sapphire, and emerald, but it is harmful to amethyst, aquamarine, and opal, which can fade their color.
13. What are the most expensive diamonds?
The most expensive diamonds are typically rare and valuable fancy color diamonds, which can command millions of dollars per carat. Some of the most famous and valuable diamonds in the world include:
The Pink Star, a 59.60-carat fancy vivid pink diamond that sold for $71.2 million in 2017.
The Oppenheimer Blue, a 14.62-carat fancy vivid blue diamond that sold for $57.5 million in 2016.
The Lesedi La Rona, a 1,111-carat diamond, from Botswana's Karowe Mine, was sold to a British jeweller for $53 million in 2017.
The Blue Moon of Josephine, a 12.03-carat fancy vivid blue diamond that sold for $48.5 million in 2015.
The Graff Pink, a 24.78-carat fancy intense pink diamond that sold for $46 million in 2010.
The Winston Blue, a 13.22-carat fancy vivid blue diamond that sold for $23.8 million in 2014.
The 3rd biggest diamond ever discovered was the Sewelo diamond, which was found at the Karowe Mine in Botswana 2019, at 1,758 carats. The 2nd biggest diamond ever discovered was in Aug. 2024, at 2,492 carats, also found in the same location, by Canadian mining company Lucara Diamond Corp. The largest, still goes to the Cullinan, at 3,106 carats, in South Africa in 1905.
14. What determines the color of a diamond?
By the presence of trace elements or structural defects within the crystal lattice of the diamond. For example, a diamond may appear red due to nitrogen vacancy in their crystal lattice structure, blue due to the presence of boron, green due to the presence of natural radiation, purple due to hydrogen, or yellow due to nitrogen.
Fancy color diamonds are graded according to their color intensity, with the most vivid and saturated colors commanding the highest prices. Red diamonds, in particular, are among the rarest and most valuable of all diamonds, with only a handful of known examples in existence.
There is a disadvantage to buying colored diamonds with intent to sell. It becomes hard to sell colored diamonds due to how hard it is to verify its authenticity.
Starting in 2019, there is an entire spectroscopy dedicated to N-vacany diamonds, where 2 carbons are replaced with 1 nitrogen next to a vacancy, which under green light, will emit red light. Called, quantum diamond microscope, it has a 5.5 eV band gap.
15. What gemstone is the most common engagement ring in the U.S.?
Diamonds are by far the most common gemstone used in engagement rings in the United States. According to a survey by The Knot in 2020, 79% of engagement rings feature a diamond as the center stone. Other popular gemstones used in engagement rings include sapphire, morganite, and aquamarine.
The Knot's 2020 Jewelry and Engagement Study surveyed nearly 21,000 U.S.-based engaged or recently married individuals aged 18 and older who were part of The Knot or WeddingWire communities.
16. Why are tourmalines green and pink or green and red?
The green is due to Cr(III) and V(III) ions, while pink is due to Mn(II) ions. Tourmalines are often green on 1 end and pink on the other, or green on the outside and pink on the inside, known as watermelon tourmaline. Sometimes, the pink turns to red, which is when Mn(II) are oxidized to Mn(III), by gamma radiation over geologic time as they sit in the Earth's crust. This gamma radiation, did not come from the atmosphere, but from the radioactive decay of 40K, in their granitic environment.
-
Identifying gemstones and precious metals.
17. What are some doping agents used in synthetic gemstones grown for the jewelry industry?
Titanium is often used to produce blue colors in synthetic sapphires. It can replace aluminum in the crystal lattice during the growth process.
Chromium is a common doping agent used to produce red or pink colors in synthetic corundum, such as synthetic rubies.
Iron impurities can contribute to the green coloration in certain synthetic gemstones.
Vanadium can be used as a doping agent to produce green or yellow colors in certain synthetic gemstones.
Neodymium is sometimes used as a doping agent to create violet or purplish colors in synthetic gemstones.
Cobalt is used as a doping agent to produce blue colors in synthetic spinel and other gemstones.
Praseodymium is often used to impart green colors in synthetic gemstones.
Holmium is known for producing a range of colors, including yellow, green, and blue, depending on its concentration and the specific crystal lattice it occupies.
Erbium is known for its ability to produce pink or rose-colored gemstones.
Gemstone manufacturers carefully control the doping process to achieve the desired color outcomes, and these colors can add variety to the range of synthetic gemstones available in the jewelry industry.
18. How are synthetic diamonds made?
By converting graphite to diamond. This was 1st done by General Electric in 1955, via a high-pressure high-temperature method, which mimics the conditions deep within the Earth, where diamonds formed naturally. General Electric used nickel as a catalyst. At that time, the pressure was done at 5-6 gigapascal, and 1500 to 2000 C, but later at Argonne Labs, was done at 10.3 gigapascal, and 2760 C.
In 1962, hydrocarbon pyrolysis was discovered, where hydrocarbon gases like methane are broken down, forming diamond structure. This method can be seen as an early form of chemical vapor deposition.
In 1972, Russian scientists discovered gas activation using hot filaments, which causes carbon to be deposited onto a substrate, where they crystallize into diamond. This technique was a major development for low-pressure diamond growth.
In 1992, Argonna Labs discovered phase-pure nanocrystalline diamonds, which have applications in coatings and optics. For example, diamond has almost 5x higher thermnal conductivity than copper, and so diamond has better heat dissipation than copper. GaN is also good for thermal management. At 80 C, 100 W/cm of GaN-on-diamond transistor arrays can be packed nearly 100x more densely than GaN-on-SiC transistor arrays, however, as of 2024, integration of diamond with GaN is challenging.
News.
11/30/2024 $83 billion worth of gold discovered in China.
Gold reserves worth 600 billion yuan, according to Reuters, which amounts to $83 billion. The discovery was made by geologists with the Hunan Provincial Geological Institute about 2 km beneath the surface in the country's Pingjiang County, Xinhua reported, according to the New York Post. The area of the discovery of 40 gold ore veins with a total of 300.2 tons of gold resources is known as the Wangu goldfield.
China is the world's largest gold producer, accounting for around 10% of global output in 2023, data from the World Gold Council showed.
Prior to the discovery, the title of the largest gold reserve in the world went to the South Deep gold mine in Gauteng Province, South Africa, the NY Post states. It holds about 930 metric tons of gold.
In March 2024, a metal detectorist in England found what might be the bigest gold nugget ever found in the country, worth an estimated $38,000, weighing 64.8 g, in Shropshire Hills. At that time, the most expensive metal detector can cost $15,000, while starter models are available for a few hundred dollars.
In 1989, a man purchased an entry-level metal detector at a Radio Shack in Mexico, then searched the Sonoran desert. He dug up the biggest gold nugget ever found in the Western hemisphere, at more than 26 lbs.
